Agile project management scrum is an iterative technique to planning and guiding the processes of the project, which divides it into smaller cycles called sprints or iterations.
Similar to Agile Software Development ( Agile ), an agile project is completed in small sections. In agile software development, for example, an iteration refers to a particular development cycle. Each section or iteration is studied and critiqued by the project team, which should include representatives from the various project stakeholders. The insights gained from critiquing an iteration are used to determine what the next step in the project should be.
The main benefit of starting with Agile scrum Project Management sprint is its ability to respond to problems that arise throughout the course of the project. Assembly a necessary change to a project at the correct time can save resources and ultimately help deliver a successful project on time and on budget.
Hello Ivy is amazingly “Simple Project Management Software” that improves Team Communication and helps you to run your entire business more efficiently. Have all your tasks, projects and team communication in one place. Manage your work, without the chaos and complexity.
Table of Contents
What is APM?
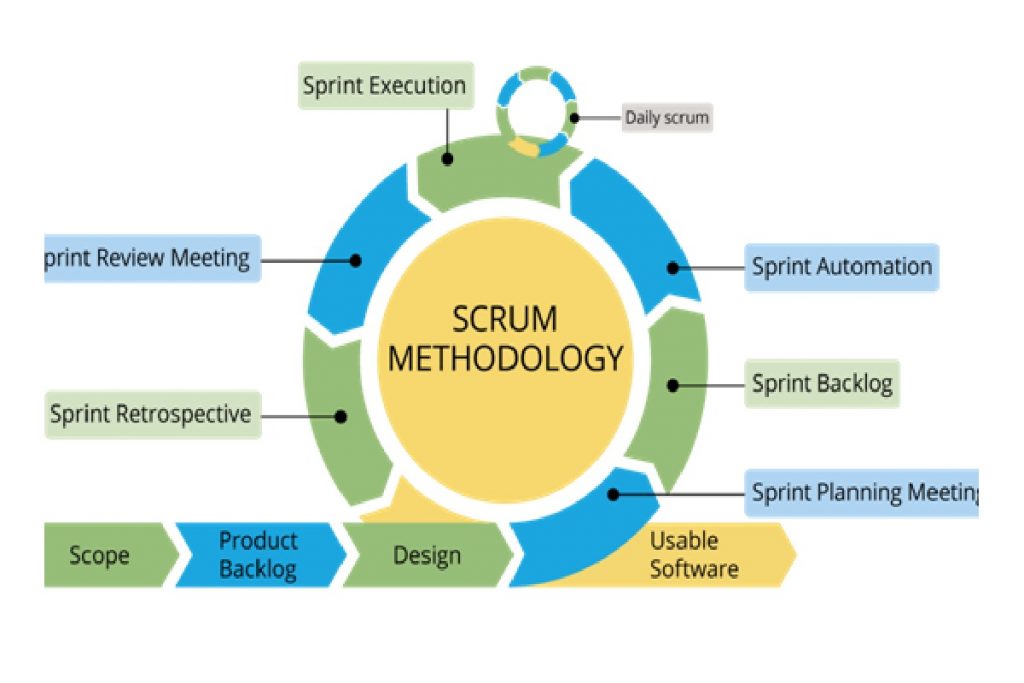
The agile project methodology divides projects into small parts — which are completed in work sessions ranging from the initial design phase through testing and quality assurance (QA). These sessions remain often referred to as sprints , the term for iteration used in a specific and popular agile development method known as Scrum.
Sprints are generally short, they take place over days or weeks; they usually last two to four weeks.
The Agile methodology allows teams to launch segments as they remain completed. This ongoing release schedule allows teams to demonstrate that these segments are successful, and if not, quickly fix failures. The belief is that these benefits reduce the possibility of large-scale failures, because there is continuous improvement throughout the project life cycle.
How the APM works
Agile teams incorporate quick feedback, continual adaptation, and quality control best practices into their iterations.
They embrace practices such as continuous deployment (CD) and continuous integration (CI), using technology that automates steps to accelerate product launch and use.
Additionally, Agile Project Management requires teams to continually assess time and cost as they progress through their work. They use speed, wear, and burn charts to measure their work, rather than Gantt charts and project milestones to track progress.
Agile project management does not involve the presence or participation of a project manager. Although a project manager is important for success under traditional project delivery methodologies such as the Cascade model (where the position manages budget, staff, project scope, quality, requirements, and other key elements) , the role of the project manager under APM is distributed among the team members.
For example, project goals are set by the product owner, while team members divide scheduling, progress reports, and quality tasks. Certain agile approaches add additional layers of management — the Scrum approach, for example, requires a scrum master to help prioritize and guide the project through to completion.
However, project managers can still remain used in agile project management. Many organizations still practice them for agile projects – particularly the larger and more complex ones – but organizations generally place these project managers in a more coordinating role, with the product owner taking responsibility for overall project completion.
Given the shift in effort from project managers to agile teams, agile project management demands that team members know how to work within this new framework. They must be able to cooperate with each other as well as with users. They must be able to interconnect well to keep projects going. And they must feel comfortable taking the appropriate actions at the right time, to keep up with delivery schedules.